TYPES OF YARN AND FIBER USED IN TEXTILE (FLAX FIBER.)
Types of yarn and fiber used in textile:-
FLAX FIBER:-
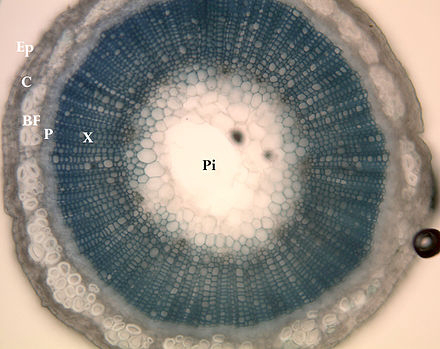
Figure, flax stem cross-section showing location of under cycling tissue,
EP=epidermis, C=Cortex, BF= Bast fiber,
P=Phloem, X=Xylem, P=Pith.
Flax fibers vary in length from about 25 to 125 mm (1to 6 inches) and average 12 to 16 micrometers in diameter. There are two varieties of it. One shorter tow fibers used for coarser fabrics, and second longer line fibers used for finer fabrics . Flax fibers can usually be identified by their "nodes" which add to the flexibility and texture of the fabrics.
DESCRIPTION:-
Several other species in the linum are similar in appearance to L.usitatissimum , cultivated flax, including some that have similar blue flowers and others with white , yellow or red flowers. Some of these are perennial plants , unlike L.usitatassimum which is an annual plant.
Cultivated flax plant grows 1.2 m(3,ft, 11 inches) tall with selender system. The leaves are glaucous green , selender , lancelate 20-40 mm long and 3mm broad.
The flowers are 15-25 mm in diameter with five petals, which can be colored white, blue, yellow and red, dry capsule 5-9 mm in diameter, contains several glossy brown seed, shaped like an apple pip 4-7 mm long.
Production method of flax fiber:-
The quality of finished linen products is often depends upon growing conditions and harvesting techniques. To generate the longest possible fibers . Flax is either hand-harvested by pulling up the entire plant or stalks are cut very close to the root . After harvesting, the plants are dried and then the seeds are removed by a mechnized process called "rippling" (thressing) and winnowing.
The fiber nust then be loosened from the stalk . This is advised through retting . This is a process which uses bacteria to decompose the pecting that binds the fibers , together. Natural retting methods take place in tanks and pools or directly in the fields. There are also chemical retting method, these are faster but are typically more harmful to the environment and to the fiber themselves.
After the retting the stalks are ready for scutching , which take place between August and December. Scutching removes the woody portion of the stalks by crushing them between two metal rollers so that the parts of the stalk can be separated. The fibers are removed and the other parts such as linseed, shives and tow are set aside for other uses. Next the fibers are hackled , the short fibers are separately with heckling combs by "combing" them away to leave behind only the long soft flax fibers.
After fibers have been separated and processed, they are typically spun in to yarns and woven or knit into linen textiles. These textiles can then be bleached , dyed dyed, printed on or finished with a number of treatment or coatings.
An alternate production method is known as "cottonizing" which is quicker and requires less equipments. The flax stalks are processed using traditional cotton machinery, however the finished fiber often lose the characterstics linen look.
Flax is growing in many parts of the world, but top quality flax is primarily grown in Western European countries and Ukrain . In recent year bulk , linen production has moved to Eastern Europe and China , but high quality fabrics are still confined to niche producers in Ireland, Italy and Belgium also in other countries including, Poland , Australia, France , Germany, Sweden , Den mark, Belarus , Lithuania, Laliva, the Netherland, Spain , Switzerland, Britain and Kochi in India . Highly quality linen fabrics are non produced in the United State for the upholstery market and in Belgium.
USES OF FLAX FIBERS:-
Flax is grown for its seeds, which can be ground into a meal or turned into linseed oil, a product used as a nutritional supplements and as an ingredients in many wood-finishing products. Flax is also grown ad an ornamental plant in ground. Moreover flax fibers are used to make linen. The specific epithet in its species name, usitatissmum mens "most usefull".
Flax fibers taken from the stem of the plants are two to three times as strong as cotton fabrics. Additionally, flax fibers are naturally, smooth and straight Europe and North America both depend on flax for plant based cloth until 19 th century, when cotton over took flax as most common play for making rag-based paper. Flax is grown on the Canadian prairies for linseed oil, which is used a drying oilnin paints and varnishes and in products , such as linoleum and printing inks.
Linseed meal , the bi-product of producing linseed oil from flax seeds, is used as like stock fodder.
Ref:-https://en.m.wikipedia.org.









Comments
Post a Comment