PICK FINDER MOTION:-
Pick Finder Motion:-
FUNCTION:-
The function of the pick finder motion is to find the pick automatically and to stop the loom when the weft breaks or run off. This is useful adjunct to the loom and is particularly useful in the multiple box looms. The pick finding is done in four revolutions of the crankshaft, as is fited with the Hattersley Standard Model Loom. For the weaving of fancy woollen and Worsted of medium and heavy weighs this loom is unsurpassed.
Special Features:-
The main features of the pick finder motion in a dobby loom may be enumerated as following:-
(1) In the multiple box loom when the weft breaks or runs off in one of the shuttles , the picking at both sides of te the loom is put out of action, but the dobby lag cylinder moves forward for that part of the revolution of the crank.
(2) The pick finder now pushes the reversing collar from the weaving to the reversing side. There it remains for two revolution of the crank shaft which turns back two lags.
(3) The reversing colour is now pushed back to the weaving side for one revolution of the crank shaft. This brings one lag forward.
(4) The loom is automatically stopped . The pick is found to be open, an the mechanism asdumes the position from which it started: just the the loom starts for weaving .
Pick Finder Mechanism:-
The mechanism which performs the useful and interesting operation of pick finding is called into play by three groups of castings , explained below. The Hattersley loom is equipped with this wonderful and ingenious pick ginder mechnism. The three groups of casting are as following:-
(1) Those attached to the brast beam :
(2) Those influence by the wheel on the bottom shaft: and
(3) Those placed on the reversing shaft under the pick finder mechanism.
These three groups of casting are initiated to their duties by the two weft forks, each being placed at a distance of 19 inches or 48.26 cm. from the center of the sleyrace. The prongs of the girl are perpendicular when the crank is at the back centre. They work almost like an ordinary weft fork.
Pick Finder Breast Beam Castings:-
Three different positions of the breast beam castings are shown in figs. 268, 269 and 270. These positions are:-
(a) The pick finder out of action (fig.268)
(b) The pik finder wih striker in action (fig.269), and
(b) Pick finder with both feelers pressed back (fig.270).
(a) Pick Finder out of Action:-
In fig.268 , two feelers A and B are placed side by side: their respective parys are shown by the straight lines . When the loom does not run, both feeler are level at the front. The lid C , with its lug under side, is raised as shown. This lid is influenced
by a swallow tailed casting , its fulcrum being at the neck. A rod passes through the tail, whilst a wing is used to raise or drop the lid , when the setting om handle is used. At G is the fulcrum upon which the connector casting oscillates . At J is the wooden block which limits the backward movement of the connector casting, after had been in sction . At H is the connecting rod which links the breast been casting with those associated with the bottom shaft. This figure gives the group of castings attatched to the breast beam. As soen , the pick finder is out of action.
(b) Pick Finder with Striker in Action:-
The figure 269 is the same as figure 268 with the addition of the striker D on the weft fork.
When the loom is started , the striker D pushes the outer of the two feelers, and leaves a gap between the two. As the
lid C has been released by the swallow-tailed casting Z , the lud Y drop between the two feelers , as shown in the figure ,
but the inner feeler B forward at E . The striker D contnues to cone opposite the pushed back feeler A, but slightly touched it.
(e) Pick finder with Both Feeles Pressed back:-
When the weft breaks or exhausted, the catch holds the cut on the weft fork , and the traverse of the striker is curtailed. This brings it opposite the inner feeler, B so that both feelers along with thelid C are forced back as in fig.270 , by the cranked end F of the striker D. This striker also moves the upper part of the casting G, elevates its lower arm, and raised the rod H. Now the pick ginde with striker is in action and with both feelers pressed back.
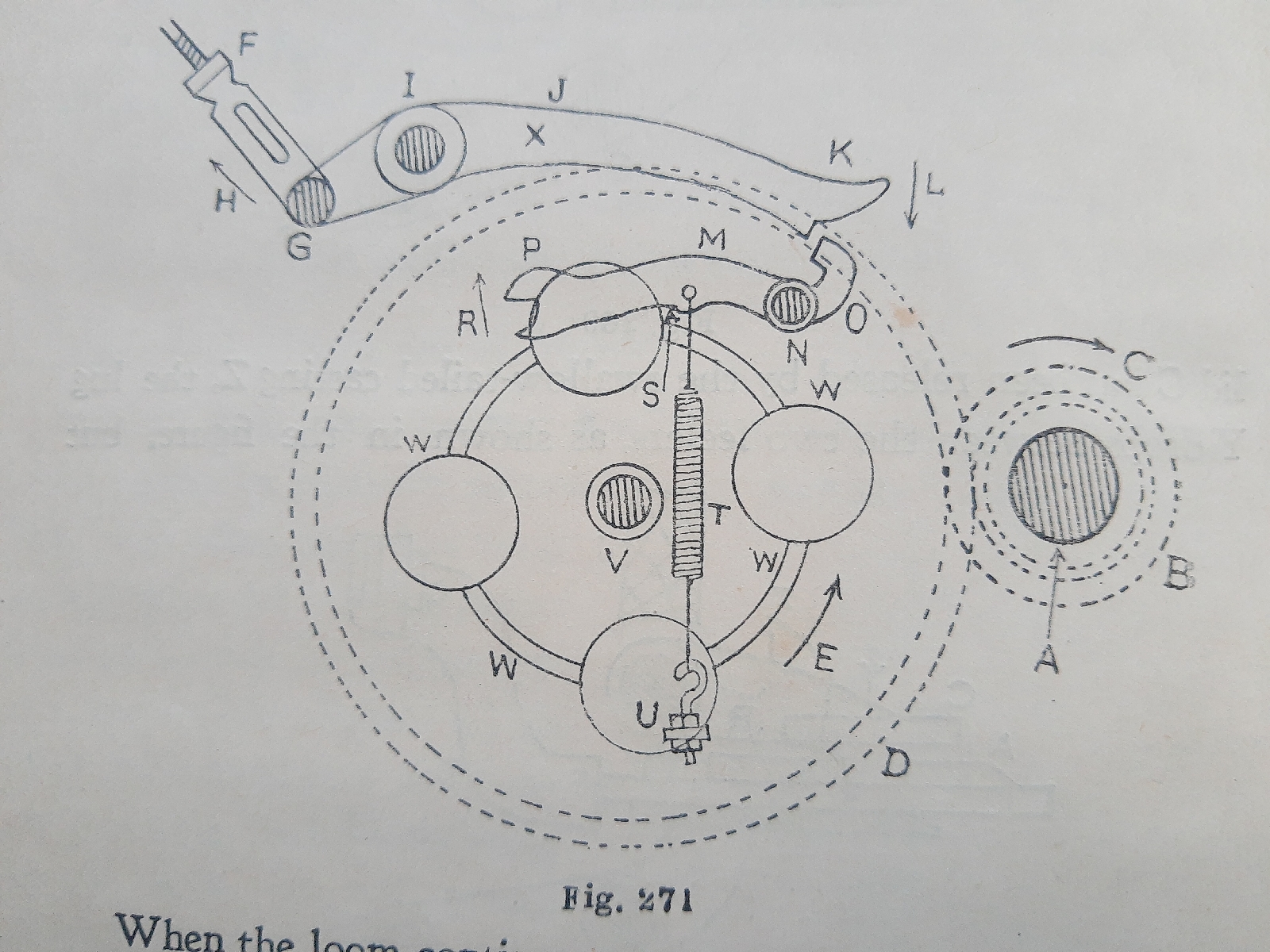
Pick Finder in Weaving Position:-
In weaving position the catch plate of the pick finder is out of action, which is outlined in fig 271. In the second group of castings A is the bottomshaft , B is clamp wheel , and C its movement and with both feelers pressed back.
When the loom contnues to weave , the spur wheel D runs and makes one revolution to four revolutions of the clamp wheel. It rotates ad shown by arrow E , but the pick finder is not affected until a weft breaks .
When weaving, the rod F moves as arrow H, and lowers the holding lever K like arrow L, and the cut on K holds the tail on key-shsped lever M and its head is elevated as arriw R . In this position the pick finder is outbof action. N is the pivot for key catch. The spur wheel and the catch plate rotates on shaft V. In some looms , the rod F is fixed to a pin at J, and the catch K is pulled up to bring the pick finder into action.
Pick Finder in action:-
When the weft fails , the weft prongs drops into their grooves and the weft fork dlidebis held by the trippler lever. This curtailed the traverse of striker. The striker comes in contact with the inner feeler presses it back, and brings the pick finder into action . When the pick finder has run its course, then it is to find the open pick after its fourth revolution.
In fig.272 the rod F is pushed down , and the lever K is lifted as at L. The tail O on the key+shaped lever M pills it down . On its underside, the key lever M gas a cut , and allows the rib W on rightnto enter and hold it. All ribs W are parys of the spur wheel D. The bottom jae of key head is shortetthan the top one , and enables if the going part is made to go back from any cause of stoppage during pick finding.
When the pick finder has run its course , the usual thing is to find the open pick on terminating its fourth revolution. It is near this termination that the rod F is pulled up, and the lever K drops, sizes the tail O and elevates the key head as at R (fig.271).
Timing:-
The special thing is the timing . It is set by setscrews on clamp wheel B. When the inner feeler on breast beam is pressed back due to weft failure , the crank is then at the front centre . In this position the key-shaped lever drops , and the rib. W, on spur wheel D, should now be just behind the forward cut S on M. This brings that pick finder motion immediately into action.
Function of Control Plate:-
The catch plate, as shown in figs. 271 and 272, is fixed by cross bolts to the control plates at fig . 273, a small space being
left between the two . Both plates move at the same time. It is seen that the control plate is heart-shaped tappet that moves as arriw E. On tje top is bowl lever G, pivoted on H, carrying bowl L , and had tod J, attached at I.
When the key lever is held byns rib on spur whel D , the movement of the heart-shaped tappet forces the bowl L out of its cavity at M , and gives the first lift to the connecting tod J . This rod is connected to the cross rod at the back base of the dobby.
The first lift of bowl is from M to N and puts picking out of action, but the lattice or lags are moved forward one leg for that turn of the crank . The second lift follows immediately from N to O, and causes the collar on the take-up shaft to move from weaving to reversing and there it remains for two revolutions of the crank shaft and two lags are truned back.
The bowl lever G then makes its first drop to P , and switches collar from reversing to weaving position, and turns one lag forward. While reversing this section the finger R, cast to the plate, contacts with the circular end of T, on lever D, swinging on thebpin Handbis forced back . On the lever S is pivoted U carrying the god V, and is moved ad arrow W. As the rod Is connected to loom handkeb, the loom stops . Before loom stopping, the Bowl L slips into cavity M and the pick finder is out of action. The control plate revolves on its fulcrum at F.
Reversing Handles:-
If the pick finder gets of order , the wravet finds the pick by using the reversible handles, as shown in fig.274.
At A is the pivot for two handles . Yo reverse , both the handles are to bre pushed over at that time. The short handl B is moved to C, and it's pin from 1 to 2.
This places picking out of action. The long handle D is moved from 3 to 4 , and the shaft and the box lages ate reversed in action. When the open pick is found , the long handle is over-centred from E to D , and the pun from 4 to 3. This makes the lags move firwatd when the crankshaft turns and the wraver then finds the open pick. Now , the short handle is moved from C to B and this pin from 2 to 1. This places the picking into action.
Effect of Picking Fork:-
At fig. 275. it is shown that the fork F at lag end of the loom is pivoted at G . Its vetical arm is slotted at H and carries a stud I, upon which the lever J moves . The rod L, moves upward where the short
reversing handle is used , and passes from B to C . This conveys K from 1 to 2, lengthenes the distance between the picking forks F and P, and both are the out of action . The figure shows how the picking fork is put out of action. Ehen the long handle is turned from D to E the lever J decends from 2 to 3 and the pivking remains outbof action ; but the reversing collar is pushed from weaving position to reversing. At N is the swivel through which the connecting rod passes , and the lock-nuts regulate it's workong length. The vertical a P is slittd at O , and the pivot of fork is at R.
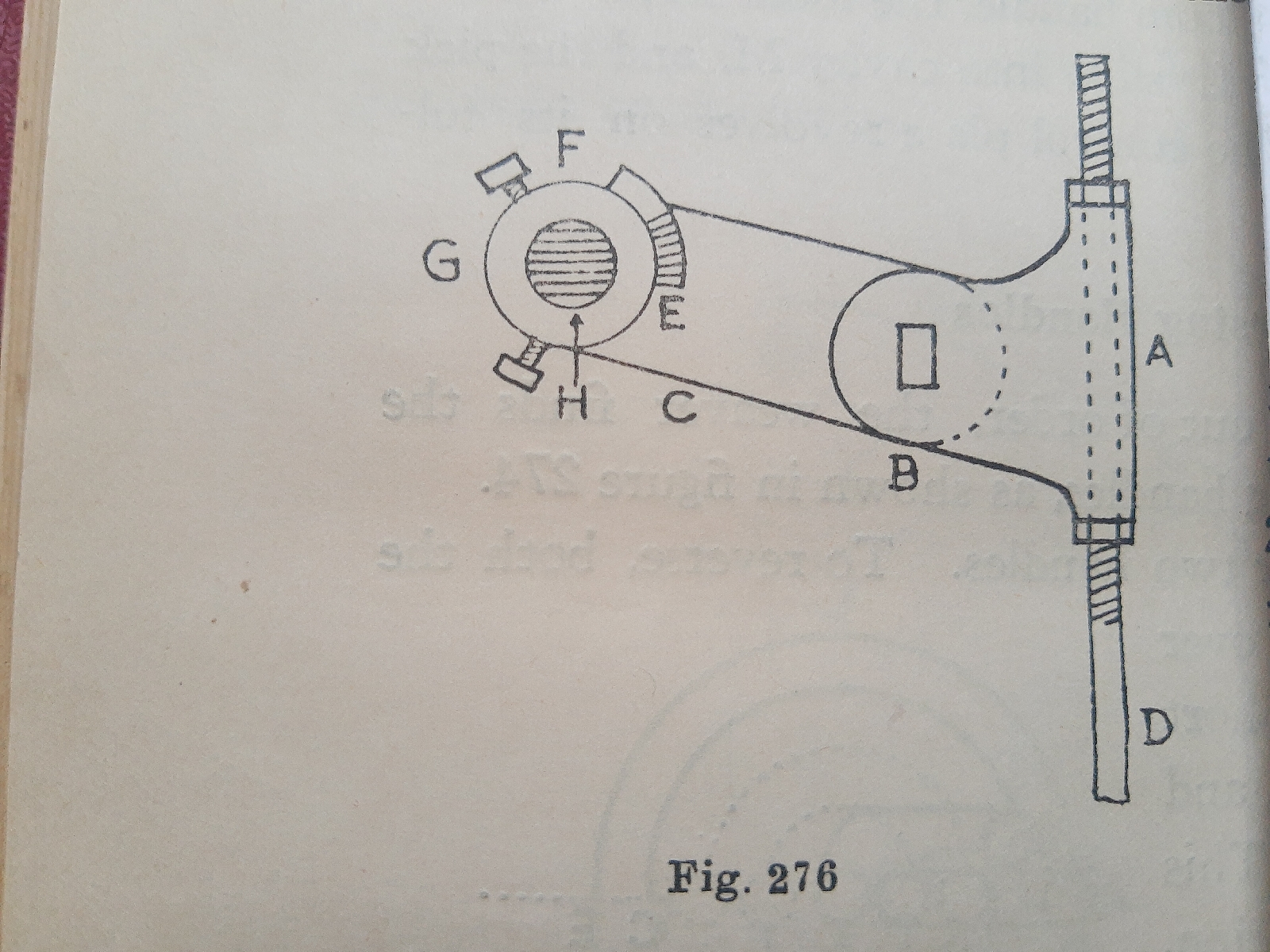
Reversing Shaft Castings:-
These casting are presented at fig. 276. In this figure the rod D is the same as the rod J in fig.273. When the inner feeler is pushed back by the striker in fig 270 , the rod D in fig. 276, is forced upward bynthe bowl lever on the heart-shaped casting in fig. 273. The rod D passes through swivel is set-sctewed to lever C, but is free to move , and C is also free on shaft H. On lever C is the lug E which is set body up to the lug F , on collar G. . By this means , the shaft H is turned by the pick finder motion
Cross Shaft Castings:-
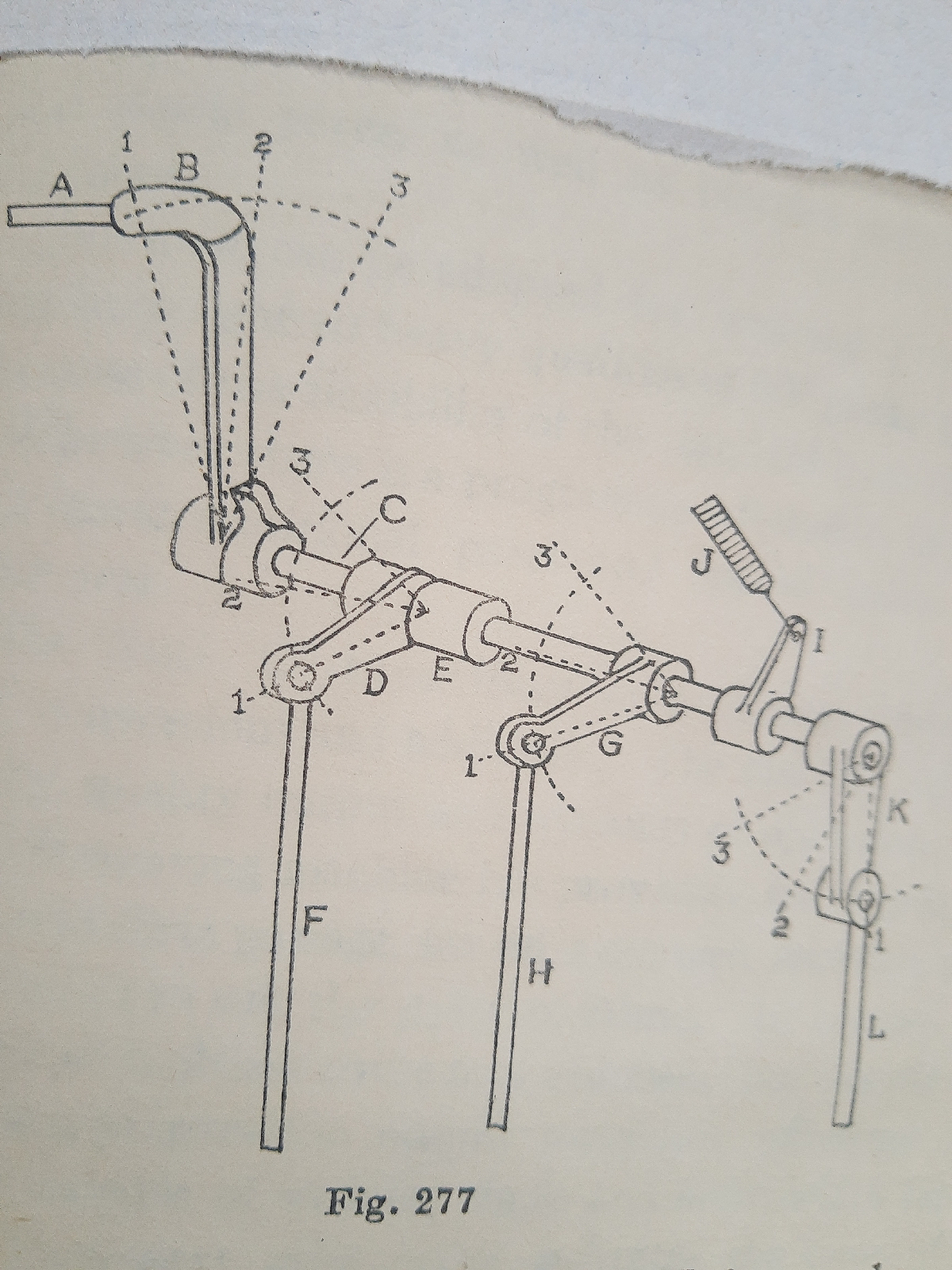
The cross shaft castingd ste depicted T fig.277
At S is the reversing rod used by the weaver. Ti is attached o the lever B with position,2 for weaving, position 3 for picking outbof action with lages moving forward, and position 3 for reversing lags without picking . The cross shaft C have five sets of casying , and the lever B is the first set.
The second set of castings is explained at fig.276, and the three positions are the same as for fig. 277.
The third casting is at G with to H that regulates the picking , and gives the same sequence of movement, as explained. The pick finder is positivt when rods F and H are lifted . The function of the lever I and J brings the shaft and rods back to their weaving positions, when the pick finishes . The fifth casting is at K. Its rid L moves the reversing collar on the take up shaft.
The five sets of casting are:- At B is the first set of casting , atbfig 376 is shown the second , at G the third , at D the fourth , and at K is seen fifth set of castings.
Reversing collar:-
A reversing collar is used with thevpick finder motion . When the loom is weaving , this collar contacts with a bevel wheel and a rod fits between the flanges on the collar. When this rod is lifted , the collar is moved to the reversing position.
Ref -Weaving Mechanism Book Vol. II by Prof. N. N. Banerjee.









Comments
Post a Comment