Semi automatic handloom (salvation army loom):-
Semi automatic handloom (salvation army loom):-
The latest and boldest step towards mechanism of the fly shuttle loom led to the invention of the a semi automatic loom. Actually, it stands between an ordinary handloom and a power loom. Some of its characteristic are exactly like a fly shuttle loom, whereas others are like power loom. Some of its motions are operated by the weaver, while others are mechanically operated. Similar looms are also in use in other states in India and on many Asian and African countries.
There are different types of semi automatic looms , they are
(1) Chitranjan Loom.
(2) Hattersley Looms.
(3) Salvation Army Loom.
Among all these three loom I have given the discussion of the above two types i.e. Chitranjan looms and Hattersley Looms. Now the third one is as under,
SALVATION ARMY LOOM.
The speciality of this type of loom rests in its picking, take-up and terry motions. For weaving a terry cloth a provision had been made for two warp beam at the back of the loom, the loose beam at the top and the fast beam at the bottom. The loose warp beam produces the terry pile in the cloth the fast beam weaves the ground.
Terry Motion:-
The mechanism to regulate the sweep of a sley to produce terry piles has been shown in fig.26
In the figure A and A' are two blocks fulcrumed at point I upon the sley-wood J. The front ends of the blocks are fastened with strings that pass over guide pulleys 2 and 3 , on the sley-sword C and C. and cross bar D respectively, to the lever Q, which is hinged upon the reed cap B. For the pile picks the lever Q is pressed down upon the reed cap B, and thereby the blocks Aand A' are raised to intervene between the sley end and a bunter on the breast beam M, at the forward movement of the sley (end elevation) and thus prevent the reed to beat-up to the fell of the cloth. For last pick, the blocks are left down. But when the sley is pulled forward, it beats up the piles picks as well as the fast pick to the fell of the cloth. Consequently, piles are formed on either side of the cloth.
Take up my motion in salvation army loom:-
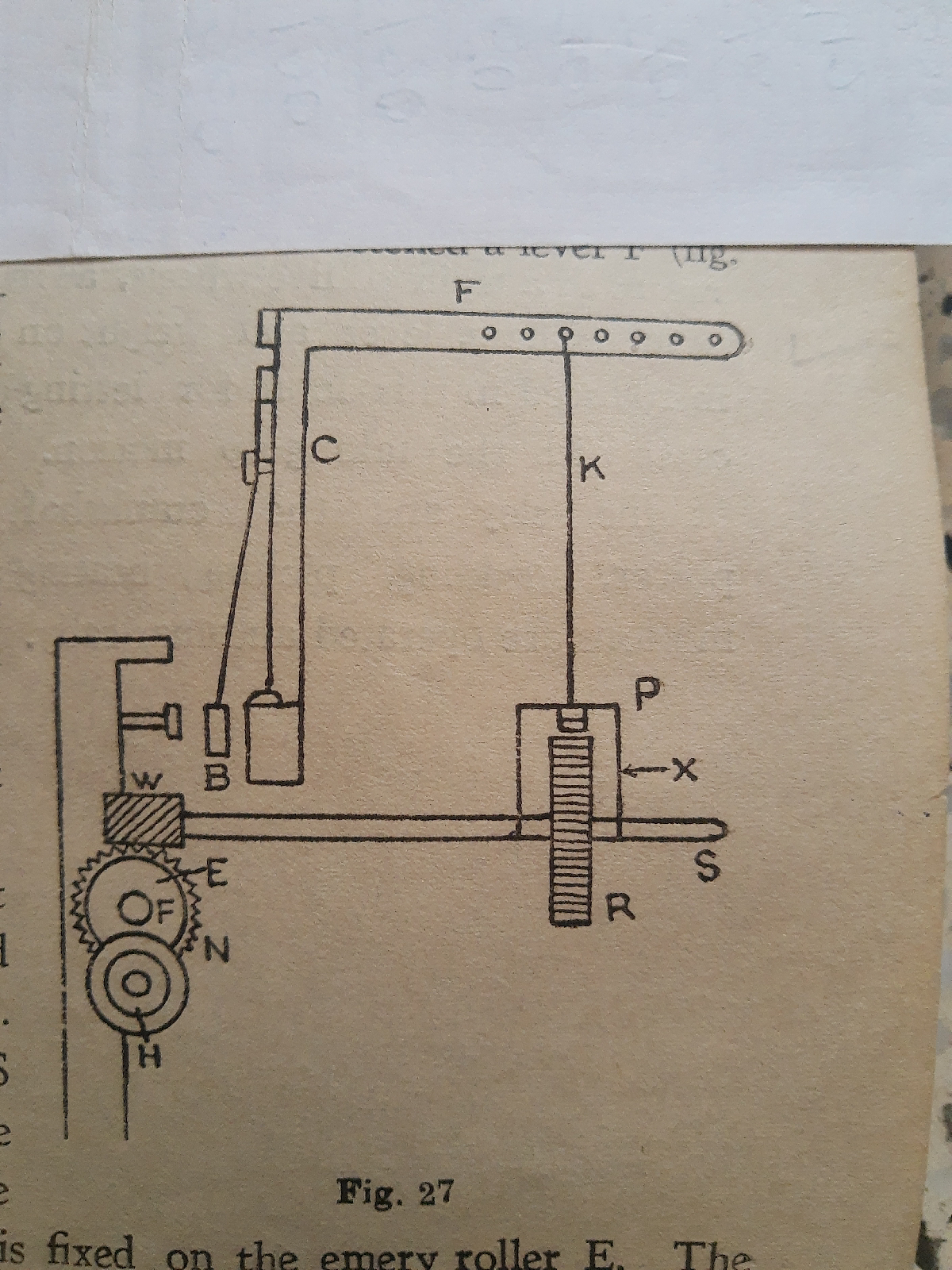
At one end of the cross bar D, is fastened a lever F (fig. 26) . A vertical connecting rod K is hooked to the lever F. The lower end of K is attached to X which carries a pushing pawl P. X is an iron plate of the shape of a box bracket freely mm mounted upon the shaft S shown in fig. 27
Now R is a ratchet wheel fixed upon S, and actuated by a pawl P. At the opposite end of S there is a worm W. The worm gears with the worm wheel N, which is fixed on the emery roller E. The cloth roller H rotates in frictional contact with the emery roller. This with the forward sweep of the sley, both the pile and ground picks are taken up on the cloth roller, the blocks being left down and lever Q up.
Ref:-Weaving Mechanism Book Vol. I by Prof. N. N. Banerjee.



Comments
Post a Comment