DOUBLE CLOTH QUALITY TESTING:-
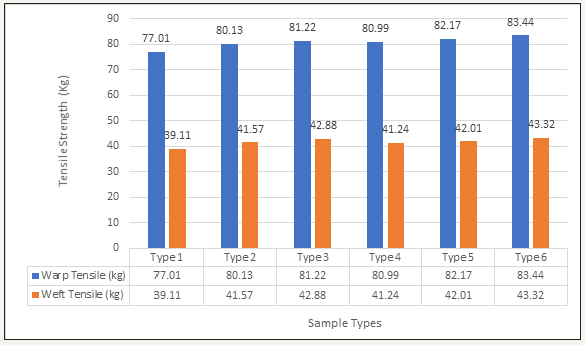
Earlier , the production and the construction ofdouble cloth is explained in my last post . Here is the samples are given in the table . Composition weight and width are also given to check different types of testing in the table for the double cloth manufactured.
Air permeability test:-
An air permeability tester was used to do this experiment. The model of the machine was FX 3300 and manufactured in Switzerland. Test pressure was 125 P a and tested area was 38cm2. The tests were done using the six types of double t works in accordance with ASTM D 737 Standard .
The unit of measurement is cm3/cm2/s. The tests were conducted with above criteria and the results are showed in Figure 13.
Figure 13:Air permeability test of different types double cloth.
Thermal conductivity test:-
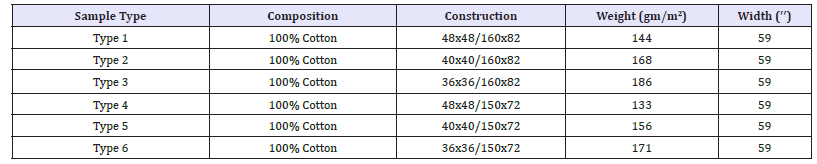
The thermal conductivity is the transfer of heat from one part of a body to another with which it is in contact. Thermal conductivity λ is defined as ability of a material to transmit heat and it is measured in watts per square metre of surface area for a temperature gradient of 1K per unit thickness of 1m. Testex TF130 auto thermal conductivity tester [10] was used to measure the thermal conductivity of the fabric at six different cloths in ASTM D1518 standard [11] as mentioned in Table 1. The composition of the fabrics tested were100% cotton. Six types of samples were used in this experiment as mentioned in the Table 1. Six thermal conductivity measurements were made for six fabrics. Ambient temperature for all measurements was 21 °C. Thermal conductivities of fabric is important for designing clothing for different climates. A fabric having a low thermal conductivity is most favorable in colder climates to prevent heat loss from the body; while in warmer climate a fabric with a higher thermal conductivity will allow heat to pass more easily from human body to help cool down. With using above criteria, thermal conductivity was tested in the lab and showed the results in Figure 14 .
Shrinkage test:-
Figure 15:Shrinkage test of double cloth.
The cotton fabric has a tendency to shrink after washing, is called shrinkage. Testex automatic shrinkage tester TF176 was used to test the shrinkage of cloth. Shrinkage rate refers to the percentage that fabrics’ size presents shrink when washed. Six different fabrics were used as mentioned in Table 1, were cut 50cm x 50cm area and 48cm x 48cm was marked with permanent marker and interlock stitching was done at the edge of the six cloths for washing and to get shrinkage test reports. ASTM D6207 standard was used to measure the fabric shrinkage [12]. Laundering includes detergent washing, normal rinse wash, extraction and drying. The process steps are- detergent wash for 90 minutes with 60 °C temperatures, rinse washed with room temperature for 45 minute and then extraction for 15 minute and at last drying for 5 minutes. Finally, shrinkage was measured by getting the length differences due to washing and showed the results in Figure 15.
Tear strength test:-
Figure 16:Measurement of tear strength.in double cloth.
“Instron 5900 tear testing machine” was used to measure the tear strength of this double cloth in ASTM D2261 Standard [13]. “3inch x 8inch” size fabrics were cut from six different types of the cloth as mentioned in Table 1 and put into the instrument for tear testing. The value of this tests were taken in gram. Using above criteria, the results of tear strengths were found and showed the consequences in Figure 16.
Tensile strength test:-
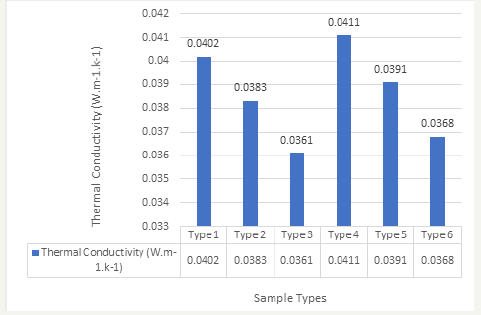
“TESTEX Tensile Testing Machine TF001” was used to measure the tensile strength of the fabric in ASTM D76 Standard [14]. “2.5- inch x 8-inch” size fabric was cut from six different types of fabrics as mentioned in the Table 1 and put to the instrument for tensile testing. The value for this test were taken in unit of kg. Using above criteria, the results of tensile strengths were found and showed the consequences in Figure 17.
Result and dis cussion:-
Results of the air permeability test
For doing air permeability testing of the different types of samples showed different results. For the sample type 1, which was cut from the double cloth of a particular portion exposed the value of 219cm3/cm2/s and showed the results in the Figure 13. For sample type 2, the value was 211cm3/cm2/s, for sample type 3, the value was 207cm3/cm2/s, for sample type 4, the value was 223cm3/ cm2/s, for sample type 5, the value was 214cm3/cm2/s. for sample type 6, the value was 210 cm3/cm2/s. It was seen that; values were different for different types of samples. It is seen for the Figure 13 that; higher air permeability was obtained for fabric of looser construction as type 1 from the Table 1. The loose the construction is, the more the value for air permeability is. The least value of air permeability was obtained for the fabric of most compact structure among the six, because compact construction disallows more air to pass therefore air permeability is less for denser qualities.
Result of thermal conductivity:-
For doing thermal conductivity testing of the different types of samples showed different results. For the sample type 1, which was cut for the double cloth of a particular portion exposed the value of thermal conductivity 0.0402 W.m-1.k-1 and showed the results in the Figure 14. For sample type 2, the value was found 0.0383 W.m- 1.k-1, for sample type 3, the value was found 0.0361 W.m-1.k-1, for sample type 4, the value was found 0.0411 W.m-1.k-1, for sample type 5, the value was found 0.0391 W.m-1.k-1.For sample type 6, the value was found 0.0368 W.m-1.k-1. It is seen from the Figure 14 that, lower thermal conductivity was obtained for the fabric of denser construction, and higher thermal conductivity value was obtained for the fabric of looser construction. Higher thermal conductivity value will allow heat to pass more easily from our body, so that faster cool down is possible. For the more compact fabrics, the thermal conductivity value is less meaning, heat will not pass so fast from fabrics.
Result of shrinkage:-
For doing shrinkage testing of the different samples showed different results. For sample type 1, which was cut for the double cloth of a portion exposed the value of warp shrinkage -2.33% and weft shrinkage -5.31% and showed the results in the Figure 15. For sample type 2, the value was found warp shrinkage -2.17% and weft shrinkage -5.23%. For sample type 3, the value was found warp shrinkage -2.11% and weft shrinkage -5.14%. For sample type 4, the value was found warp shrinkage -2.43% and weft shrinkage -5.41%. For sample type 5, the value was found warp shrinkage -2.31% and weft shrinkage -5.32%. For sample type 6, the value was found warp shrinkage -2.03% and weft shrinkage -5.22%. It is seen from the Figure 15 that; more shrinkage values were obtained for the fabrics of looser constructions and less shrinkage values were obtained for the fabrics of compact constructions. Compact constructions shrink less when it come in contact of water, on the other hand, loose constructions shrink more when it come in contact of water.
Result of tear strength:-
For doing tearing testing of the different types of samples showed different results. For the sample type 1, which was cut for the double cloth of a particular portion exposed the value of warp tear 7913gram and weft tear 4850 gram and showed the results in the Figure 16. For sample type 2, the value was found warp tear 8201gram and weft tear 5023gram. For sample type 3, the value was found warp tear 8411gram and weft tear 5133gram. For sample type 4, the value was found warp tear 8031gram and weft tear 4798gram. For sample type 5, the value was found warp tear 8333gram and weft tear 5001gram.For sample type 6, the value was found warp tear 8501 gram and weft tear 5233. It is seen from the Figure 16 that, higher tear strengths are obtained for the fabrics of heavier weight and lower tear strengths are obtained for the fabrics of lesser weights. It is clear that, heavier fabrics have more tear strength.
Result of tensile strength:-
For doing tensile testing of the different types of samples obtained different results. For sample type 1, which was cut for the double cloth of a portion exposed the value of warp tensile 77.01kg and weft tensile 39.11kg and showed the results in the Figure 17. For sample type 2, the value was found warp tensile 80.13kg and weft tensile 41.57kg. For sample type 3, the value was found warp tensile 81.22kg and weft tensile 42.88kg. For sample type 4, the value was found warp tensile 80.99kg and weft tensile 41.24kg. For sample type 5, the value was found warp tensile 82.17kg and weft tensile 42.01kg. For sample type 6, the value was found warp tensile 83.44kg and weft tensile 43.32kg. It is seen from the Figure 17 that; higher tensile strengths are obtained for the fabrics of heavier weight and lower tensile strengths are obtained for the fabrics of lesser weights. It is clear that, heavier fabrics have more tensile strength.
Conclusion:-
At last it can be concluded that, double cloth is a type of advanced weave with an advanced construction that creates two textiles, one above the other by means of at least two sets of warps and two sets of weft. A woven fabric construction made by interlacing two or more sets of warp yarns with two or more sets of filling yarns. Double weave is a family of weave styles in which the face of the fabric is effectively detached from the back except at specific connecting interlacing, yet with each side maintaining sufficient individual structural integrity to be identified as distinct fabrics in itself. These fabrics are met in both decorative and utilitarian roles and inhabit interesting excesses at either end of those spectra. Double cloth fabrics were produced by self-stitching, center stitching and by thread interchange which all were discussed in this project. Construction of Self-stitched double cloths can be produced by stitching from face to back, stitching from back to face and by combination stitching all were discussed briefly in this project. Double cloth fabric can also be produced by waded yarns in both warp and weft way. Higher air permeability obtained for fabric of looser construction useful for the body. In case of more compact fabrics, thermal conductivity value was less so that heat will pass slowly for this fabric types. Shrinkage values are less for the fabrics of denser constructions. Higher strengths obtained for the fabrics of heavier weight. Specially, air permeability and thermal conductivity can be improved significantly through the production of double cloths
ref:-https://crimsonpublishers.com.










Comments
Post a Comment